Unit 4 Employee Loyalty + Leadership

Photo by Yan Krukov from Pexels
Overview
Congratulations on completing Unit 3. In unit 4, you will learn that employee loyalty and engagement are based on three primary levers. Organization Leadership (CEO), Human Resources (HR) Department, and Supervisory Leadership Team (MBS). A different approach is taken when it comes to assessing performance by HR. Employee engagement and performance are measured for effectiveness and efficiency depending on how HR defines performance in the organization. Peters’ textbook (2019, pp. 207-214) suggests that HR in organizations must understand both the role of individuals and the collective construct of employee engagement before evaluating performance outcomes.
This unit is divided into the following topics:
- Full Spectrum Leadership;
- MBS Leadership Team;
- Organizational Culture, Leadership, and Employee Performance & Satisfaction.
Learning Outcomes
When you have completed this unit, you should be able to:
- Take into consideration a spiritual model of leadership and transformational servant leadership in relation to the engagement and stewardship of people.
- Reflect critically on the engagement practices and stewardship responsibilities of leaders in relation to their organization’s human resources (people), in terms of both the task and the people factors.
- Analyze an organization’s engagement and stewardship practices to determine how effective and ineffective they are.
- Employ best practices to create a high level of employee loyalty.
Assess the role of the leadership team, the Human Resources Department, and immediate supervisors in creating high employee loyalty.
4.1 Full Spectrum Leadership
A company’s leadership plays a critical role in creating an environment where employees can perform well. Good leadership provides opportunities for positive engagement experiences in three facets: intellectual, social, and affective (ISA) engagement.
Full Spectrum Leadership (Peters, p. 152) was introduced by Richard Barrett (2011) in his book “The New Leadership Paradigm” and researched and embedded into full-scale leadership development programs by the Barrett Values Centre. Full Spectrum Leadership is about mastering and displaying the attributes of the seven levels of organizational consciousness: (also see this link, para(s). 1-5)
- Survival Level: mastering survival consciousness by focusing on financial stability and employee health and safety (both physical and psychological).
- Relationship Level: mastering relationship consciousness by focusing on open communication, employee recognition, and customer satisfaction.
- Self-Esteem Level: mastering self‐esteem consciousness by focusing on performance, results, quality, excellence, and best practices.
- Transformation Level: mastering transformation consciousness by focusing on adaptability, innovation, employee empowerment, employee participation, and continuous learning.
- Internal Cohesion Level: mastering internal cohesion consciousness by developing a culture based on a shared vision and shared values that engender an organization‐wide climate of trust.
- Making a Difference Level: mastering making a difference consciousness by building strategic alliances with like‐minded partners, developing mentoring, coaching and leadership development programs for their managers and leaders, and embracing environmental stewardship.
- Service Level: mastering service consciousness by focusing on social responsibility, ethics, global thinking, and keeping a long‐term perspective on their business and its impact on future generations.
Each level of consciousness has a corresponding leadership style and each leadership style is governed by certain primary motivations. Primary motivations are the immediate and conscious focus of the leader, which will critically determine where his/her energy will be focused. Here’s a visual representation: (Source from Let’s - talk).
The most successful leaders are those who have learned to master all levels of consciousness. They create a climate of trust, have the ability to manage complexity, and can respond or rapidly adapt to all situations, all the while keeping a strong and sustainable vision of the future. People that work with full spectrum leaders operate with honesty and integrity, because they are encouraged to do so. The leaders act as role-models and they set up systems and processes that encourage ethical behavior, collaboration and effort towards common good.
4.2 MBS Leadership Team
In an organization, MBS represents managers, bosses, and supervisors. From the very top, the Chief Executive Officer (CEO). It is the CEO and team’s responsibility to build the company’s vision and mission.
The company’s purpose and direction (roadmap) are established in three ways:
- Define and establish a clear Vision/Mission and align the organization to its Vision/Mission/Purpose. In doing so, the leadership produces four positive outcomes for the organization and its employees;
- Focus & direction in an ever-changing environment;
- Proactive & Accomplishment towards achieving the purpose;
- Teamwork & Relationships going the same direction for the a common cause;
- Constancy in how it manages both external and internal change.
- Focus & direction in an ever-changing environment;
- Identify and manage the core values of the organization. The values determine the way Business/Industry is conducted within the organization on a day-to-day basis, both internally and externally. They guide the practices that ensure the eleven factors are practiced and maintained. They ensure that all processes and policies are aligned with the values of the organization. These values can be placed into two categories:
- Organic Values: which are the principles and or philosophies that guide the way in which the organization’s purpose will be met. These values never change.
- Operating Values which define the way the organization will operate in the current business environment. These values can change when necessary.
- Organic Values: which are the principles and or philosophies that guide the way in which the organization’s purpose will be met. These values never change.
- Serve as Inspiring Role Models. Essentially the leadership practices what they preach, and live out in themselves what they expect of their organization and employees. They set the example for the team to follow. The ultimate goal of the MBS is to ensure that every person is giving their best in their job and to the organization. They do this in a number of ways, the following are some of them:
- Provide job clarity and clear expectations.
- Remove any barriers to success for each employee.
- Provides coaching to improve job satisfaction and sense of accomplishment.
- Shows regular recognition and appreciation.
- Look for and provide opportunities for individual development.
- Clear communication conduit to and from the Organizational Leadership.
- Lead by example.
- Provide job clarity and clear expectations.
The HR department for organizations plays an important role as well although they are not traditionally considered as a part of MBS; however, they are important to support MBS to implement their functions for organizations. In general, the HR Department for any organization has five critical roles to play creating high employee engagement/loyalty.
- HR creates its operational structure and ensures that the overall organizational structure is completely aligned to the purpose of the organization.
- HR ensures that all organizational and HR policies and procedures are in sync with the organization’s values, and that those policies are understood and practiced at all levels in the organization.
- HR provides training, mentoring and ongoing support for the managers and employees in keeping with the organizational Mission/Vision/Purpose and Values, and insuring that the important factors, such as Rao’s eleven factors, are practiced and experienced.
- HR facilitates the organization to form a culture aligned with the vision/purpose/values of the organization.
- HR is responsible for the outcome measurement process for the organization to ensure the outcome measurement process (for example, employee performance outcome) is implemented according to the mission/purpose/values of the organization.
4.3 Organizational culture, Leadership, and Employee Performance and Satisfaction
An organization’s culture plays an important role. Think about the impact of culture on employee performance and satisfaction using the following. An organization’s culture plays a major role in employee engagement. The culture of an organization may be supportive/unsupportive or positive/negative. In organizations with a positive culture, employees are rewarded and an enabling environment is created where they can grow, develop, and perform at their best (Robbins & Judge, 2012).
View the graph below to understand the possible dimensions of organizational culture.
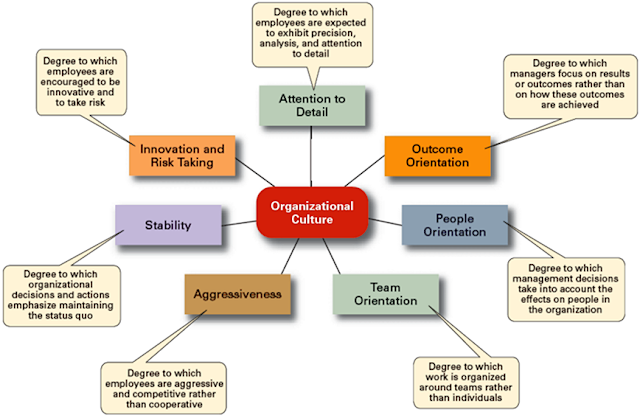
Source: Robins, S., Coulter, M. (2007). Organizational culture and environment: The constraints. Management (11th Ed.), (p. 3). US: Prentice Hall Publishing.7
The following graph, is a to understand the role organizational culture plays in employee engagement and job satisfaction.
Source: Source: Robins, S., Judge, T. (2011). Organizational culture. in Organizational Behavior (14th Ed.), Power Point Slides (p.18). US: Prentice Hall Publishing.
The third graph is shown to help you understand the complexity of leadership, including self-awareness and leadership style in the process of changing organizational culture.
Source: Crowell, D. (2016). Complexity leadership: Nursing’s role in healthcare delivery (2nd Ed.). (page 5). F.A. Advis Company. https://eds.a.ebscohost.com
Learning Activity: Reflect and Respond
- You have learned about Organizational culture, Leadership, and Employee Performance and Satisfaction as a potential TSL leader. Additionally have learned the skills to observe and examine the signs of engagement, disengagement, culture, MBS leadership, and your leadership style. Answer to the following questions.
Summary
The success of any organization and its employee engagement ultimately hinges on those who lead and manage the team/company/organization. In this unit, the definition of MBS and their functions are clearly defined and discussed in Topic 1 and Topic 2. The identification and declaration of an organization’s mission/values/purpose is not enough.
The leadership team of any organization must embrace, encourage, and model to their employees within the organization and to the key external stakeholders that include the customer, investors, suppliers, and community at large. In addition, the HR for organizations plays a critical role to ensure the functions of the leadership team can be implemented for effective employee engagement/loyalty/culture for the organization. As a potential TSL leader, your leadership skills can be practiced at any level regardless of the title you have. They are important skills to have because a good leader can bring out the best abilities in his/her team members and motivate them to work together in achieving a shared goal. The outcome of good leadership generates positive and meaningful employee engagement and corporate culture for all employees and the organization.
References
- Ariussanto, K., Tarigani, Z., Sitepu, R., & Singh, S. (2020). Leadership style, employee engagement, and work environment to employee performance in manufacturing companies. SHS Web of Conferences, 76(01020). https://doi.org/10.1051/shsconf/20207601020
- Block, P. (2013). Stewardship: Choosing service over self-interest (2nd ed.). Berrett-Koehler Publishers. https://www.bkconnection.com/static/Stewardship_2nd_EXCERPT.pdf
- Bridger, E. (2018). Employee engagement: A practical introduction.
- Grimm, R. (2017). The link between leadership style and job satisfaction in the Don Civilian Workforce. Doctorate dissertation, Liberty University https://digitalcommons.liberty.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?referer=https://scholar.google.com/&httpsredir=1&article=2696&context=doctoral
- Peregrym, D. (2011). The consideration of spiritual leadership. Summary of [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Trinity Western University.
- Peters, J. (2019) (Chapters 4 & 8) - Employee Engagement: Creating High Positive Energy at Work (eBook).